By Dr. Courtney Conley (DC, BS in Kinesiology & Human Biology)
The difference between Tendonitis and Stress Fractures
Tendonitis and stress fractures are common foot injuries that can cause pain, limit mobility, and affect daily activities. Understanding their differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
In this guide, we’ll break down what each condition is, why it matters, and how to manage and prevent them - so you can keep moving without pain.
Tendonitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
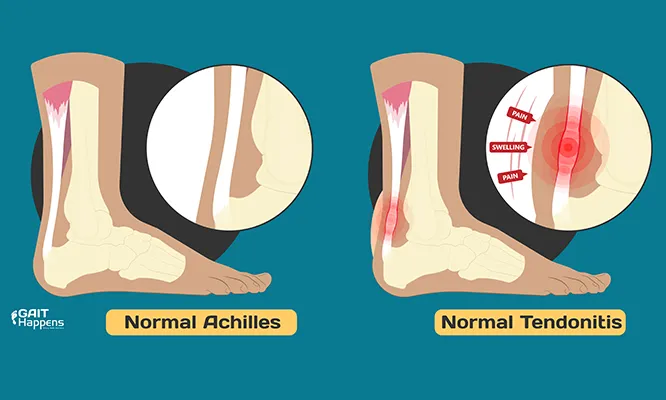
What is Tendonitis
Tendonitis is inflammation or irritation of a tendon (the cord connecting muscle to bone). In the foot, this can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness especially during movement.
Common Tendonitis Causes
- Overuse from running, jumping, or prolonged standing
- Improper footwear 👟
- Structural issues like flat feet or high arches when associated with weakness or restrictions in mobility
- Age-related tendon degeneration
- Previous injuries
Common Tendonitis Symptoms
- Persistent or activity-related pain
- Swelling and tenderness
- Stiffness, especially after rest
- Limited range of motion
- Warmth or redness over the tendon
Diagnosis of Tendonitis
A clinician will review your history, examine the foot, and may order imaging (ultrasound or MRI) to assess the tendon. Something to keep in mind is that tendon structure is not the end all be all. We shouldn't chase what we see on the imaging for rehabilitation purposes. There are many times that the imaging will not improve even if the symptoms have decreased.
Tendon structure tends to carry more clout in the elite athlete more so than the everyday person as changes in the tendon in the beginning of the season can be a good predictor of injury during the season.
Treatment for Tendonitis
- Activity modification (tendons need progressive loading to heal) Loads of 90% MVC needs to be used to induce structural changes of the tendon
- Gentle mobility & strengthening exercises
- Footwear adjustments which is very context dependent based on individual goals and past medical history.
💡 For guided recovery, our Fit Feet Program offers a 12-week, clinician-designed plan to improve strength, mobility, and resilience in your feet and lower legs.

Stress Fractures: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What are Stress Fractures?
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in the bone, usually caused by repetitive impact over time - not a single traumatic event. Common sites include the metatarsals and heel.
How Stress Fractures Occur
- Overuse or repetitive high-impact activity
- Sudden increase in training volume
- Inadequate footwear or shock absorption
- Structural imbalances (flat feet, high arches)
- Nutritional deficiencies (calcium, vitamin D)
- Female Athlete Triad risk factors
Symptoms of a Stress Fracture
- Localized pain that worsens with weight-bearing
- Swelling over the fracture site
- Bruising (sometimes)
- Point tenderness when pressing on the area
Diagnosis of a Stress Fracture
X-rays may miss early fractures - MRI or bone scans are often needed for confirmation.
Treatment for Stress Fractures
- Rest & immobilization (walking boot, crutches)
- Protected weight-bearing under clinical guidance
- Gradual return to activity once healed
- Strength and gait retraining to prevent recurrence
- It is important to identify where in the foot the stress fracture occurs as some sites are prone to compressive loading and others tensile strain. The treatment approach should be geared towards the underlying cause.
👣 Want to reduce the risk of stress fractures long-term? Our Sole Switch Course teaches you how to transition to healthier footwear safely while building foot strength.

Prevention Tips for Tendonitis and Stress Fractures
- Warm up & stretch before activity
- Progress training gradually
- Cross-train with low-impact activities 🚴🏊
- Choose footwear that allows your foot to get stronger! Transition wisely to more minimal footwear ONLY when fractures and acute symptoms have healed.
- Rest & recover between intense sessions
- Maintain good nutrition and hydration 💧
When to Seek for Tendonitis and Stress Fractures
If foot pain persists, worsens, or limits daily activities, it’s best to get a professional evaluation. Early intervention prevents small problems from becoming chronic injuries.
Bottom Line
Both tendonitis and stress fractures require timely attention and a tailored recovery plan. Tendonitis affects the tendons; stress fractures involve the bone, but both can keep you sidelined without proper care.
By understanding the differences, recognizing early symptoms, and using targeted prevention strategies, you can protect your feet and stay active for the long run.